A Way To Manage Pes Planus
Overview

Some people have always had flat feet from a young age. Unfortunately as people reach their fifties they will suddenly have one foot with a flatter arch than the other foot. This situation is termed adult acquired flatfoot. Adult acquired flatfoot is a painful condition occurring in one foot. The common patient profile is a female over the age of 50 with pre-existing flatfeet, high blood pressure, high cholesterol, diabetes and obesity. All of these underlying problems will lead to a weakening of the support structures of the arch. If you have adult acquired flat foot you will not be able to lift your heel off the ground while standing on one leg. Adult acquired flatfoot may develop due to trauma or degeneration of major tendons ankle & foot. Weakness or paralysis of leg muscles can also create a flatfoot deformity. Adult acquired flat foot can be treated with physical therapies, motion control running shoes or hiking boots, custom foot orthoses, and ankle foot orthoses.
Causes
As children grow, their legs will experience developmental changes that can result in excess flattening of the arches with weight bearing. One example is genu valgum, or knock-knees, a usually normal, temporary condition in children at different stages of growth. A tight calf muscle or Achilles tendon can also contribute to a flat foot. Many children will experience tight calf muscles as they go through growth spurts. Conditions that are present at birth and are often diagnosed early include: metatarsus adductus, calcaneovalgus and congenital vertical talus. Tarsal coalitions are congenitally fused foot bones that cause a rigid flat foot often associated with painful muscle spasms. This type of flat foot is usually diagnosed later in childhood or in adulthood. Any condition that causes loose ligaments can result in a flat foot or lower-than-normal arch. Ligaments are bands of tissue that connect bones to each other and have an important role in giving form to foot arches. An example of a condition that causes loosening of ligaments is pregnancy, where normal hormonal changes relax the ligaments. Diseases that cause loose ligaments include Ehlers-Danlos syndrome, Marfan's syndrome and rheumatoid arthritis. If one leg is longer than the other, one foot may be flat in relation to the other to compensate. Usually the foot on the longer limb will have a flatter arch in an effort to shorten that limb, balancing-out the unevenness. Leg length inequality can be caused by spinal abnormalities such as scoliosis. It can also be due to an actual difference in length of one leg bone compared to the other.
Symptoms
Knee/Hip/Back Pain - When the arch collapses in the foot, it triggers a series of compensations up the joint chain, leading to increased stress on the knee, pelvis and low back. Plantar fasciitis - This condition is characterized by heel pain, especially with the first few steps you take. The plantar fascia stretches as the arch falls, putting stress on the heel. Bunions - If you see a bony bump developing at the base of your big toe, you are likely developing a bunion. It may be swollen, red or painful when it rubs against your shoe. A flattened arch spreads the forefoot and causes the big toe to deviate toward the second toe. Shin splints - This term generally refers to pain anywhere along the shinbone. It is typically due to overuse and is aggravated after exercise and activity.
Diagnosis
Your doctor will ask about your symptoms and medical history. A physical and foot exam will be done. Flat feet can be diagnosed by appearance. To determine if the foot is rigid, you may be asked to do some simple tasks.
fallen arches insoles
Non Surgical Treatment
If the flat foot is rigid and causing problems, you will be referred to a foot specialist. Talk with your doctor about the best treatment plan for you. Options include the following. Physical Therapy and Exercises. Physical therapy may relieve discomfort. You may be given a specific stretching and strength program. You may also have treatment to help manage the discomfort. Exercises can help with the strength of the surrounding muscles. It may relieve some of the pressure in the foot. Orthotics are shoe inserts that support the foot. These inserts may help to reduce pain and disability in some people. In mild cases, a well-fitting pair of shoes with arch support may be all that is needed. Flat feet caused by nerve or muscle disease may need special braces. Fallen arches are usually treated using stretching exercises, physical therapy and medication (to reduce inflammation). In extreme cases however, surgery is recommended.
Surgical Treatment

This is rare and usually only offered if patients have significant abnormalities in their bones or muscles. Treatments include joint fusion, reshaping the bones in the foot, and occasionally moving around tendons in the foot to help balance out the stresses (called tendon transfer).
After Care
Time off work depends on the type of work as well as the surgical procedures performed. . A patient will be required to be non-weight bearing in a cast or splint and use crutches for four to twelve weeks. Usually a patient can return to work in one to two weeks if they are able to work while seated. If a person's job requires standing and walking, return to work may take several weeks. Complete recovery may take six months to a full year. Complications can occur as with all surgeries, but are minimized by strictly following your surgeon's post-operative instructions. The main complications include infection, bone that is slow to heal or does not heal, progression or reoccurrence of deformity, a stiff foot, and the need for further surgery. Many of the above complications can be avoided by only putting weight on the operative foot when allowed by your surgeon.

Some people have always had flat feet from a young age. Unfortunately as people reach their fifties they will suddenly have one foot with a flatter arch than the other foot. This situation is termed adult acquired flatfoot. Adult acquired flatfoot is a painful condition occurring in one foot. The common patient profile is a female over the age of 50 with pre-existing flatfeet, high blood pressure, high cholesterol, diabetes and obesity. All of these underlying problems will lead to a weakening of the support structures of the arch. If you have adult acquired flat foot you will not be able to lift your heel off the ground while standing on one leg. Adult acquired flatfoot may develop due to trauma or degeneration of major tendons ankle & foot. Weakness or paralysis of leg muscles can also create a flatfoot deformity. Adult acquired flat foot can be treated with physical therapies, motion control running shoes or hiking boots, custom foot orthoses, and ankle foot orthoses.
Causes
As children grow, their legs will experience developmental changes that can result in excess flattening of the arches with weight bearing. One example is genu valgum, or knock-knees, a usually normal, temporary condition in children at different stages of growth. A tight calf muscle or Achilles tendon can also contribute to a flat foot. Many children will experience tight calf muscles as they go through growth spurts. Conditions that are present at birth and are often diagnosed early include: metatarsus adductus, calcaneovalgus and congenital vertical talus. Tarsal coalitions are congenitally fused foot bones that cause a rigid flat foot often associated with painful muscle spasms. This type of flat foot is usually diagnosed later in childhood or in adulthood. Any condition that causes loose ligaments can result in a flat foot or lower-than-normal arch. Ligaments are bands of tissue that connect bones to each other and have an important role in giving form to foot arches. An example of a condition that causes loosening of ligaments is pregnancy, where normal hormonal changes relax the ligaments. Diseases that cause loose ligaments include Ehlers-Danlos syndrome, Marfan's syndrome and rheumatoid arthritis. If one leg is longer than the other, one foot may be flat in relation to the other to compensate. Usually the foot on the longer limb will have a flatter arch in an effort to shorten that limb, balancing-out the unevenness. Leg length inequality can be caused by spinal abnormalities such as scoliosis. It can also be due to an actual difference in length of one leg bone compared to the other.
Symptoms
Knee/Hip/Back Pain - When the arch collapses in the foot, it triggers a series of compensations up the joint chain, leading to increased stress on the knee, pelvis and low back. Plantar fasciitis - This condition is characterized by heel pain, especially with the first few steps you take. The plantar fascia stretches as the arch falls, putting stress on the heel. Bunions - If you see a bony bump developing at the base of your big toe, you are likely developing a bunion. It may be swollen, red or painful when it rubs against your shoe. A flattened arch spreads the forefoot and causes the big toe to deviate toward the second toe. Shin splints - This term generally refers to pain anywhere along the shinbone. It is typically due to overuse and is aggravated after exercise and activity.
Diagnosis
Your doctor will ask about your symptoms and medical history. A physical and foot exam will be done. Flat feet can be diagnosed by appearance. To determine if the foot is rigid, you may be asked to do some simple tasks.
fallen arches insoles
Non Surgical Treatment
If the flat foot is rigid and causing problems, you will be referred to a foot specialist. Talk with your doctor about the best treatment plan for you. Options include the following. Physical Therapy and Exercises. Physical therapy may relieve discomfort. You may be given a specific stretching and strength program. You may also have treatment to help manage the discomfort. Exercises can help with the strength of the surrounding muscles. It may relieve some of the pressure in the foot. Orthotics are shoe inserts that support the foot. These inserts may help to reduce pain and disability in some people. In mild cases, a well-fitting pair of shoes with arch support may be all that is needed. Flat feet caused by nerve or muscle disease may need special braces. Fallen arches are usually treated using stretching exercises, physical therapy and medication (to reduce inflammation). In extreme cases however, surgery is recommended.
Surgical Treatment

This is rare and usually only offered if patients have significant abnormalities in their bones or muscles. Treatments include joint fusion, reshaping the bones in the foot, and occasionally moving around tendons in the foot to help balance out the stresses (called tendon transfer).
After Care
Time off work depends on the type of work as well as the surgical procedures performed. . A patient will be required to be non-weight bearing in a cast or splint and use crutches for four to twelve weeks. Usually a patient can return to work in one to two weeks if they are able to work while seated. If a person's job requires standing and walking, return to work may take several weeks. Complete recovery may take six months to a full year. Complications can occur as with all surgeries, but are minimized by strictly following your surgeon's post-operative instructions. The main complications include infection, bone that is slow to heal or does not heal, progression or reoccurrence of deformity, a stiff foot, and the need for further surgery. Many of the above complications can be avoided by only putting weight on the operative foot when allowed by your surgeon.
Heel Discomfort Everything You Should Understand Heel Aches
Overview

When walking, your heels repeatedly hit the ground with considerable force. They have to be able to absorb the impact and provide a firm support for the weight of the body. When pain develops in the heel, it can be very disabling, making every step a problem, affecting your posture. There are various types of heel pain. Some of the most common are: heel spurs (plantar fasciitis); heel bursitis and heel bumps.
Causes
Rheumatoid arthritis and other forms of arthritis, including gout, which usually manifests itself in the big toe joint, can cause heel discomfort in some cases. Heel pain may also be the result of an inflamed bursa (bursitis), a small, irritated sack of fluid behind the heel. A neuroma (a nerve growth) involving the so-called Baxter's Nerve, (a nerve that courses under the heel bone), may also cause heel pain that mimics the pain of a heel spur. Tarsal Tunnel Syndrome, a pinched nerve beneath the inside ankle bone, too, can cause pain in the heel. Haglund's deformity ("pump bump") is a bone enlargement at the back of the heel bone, in the area where the Achilles tendon attaches to the bone. This sometimes painful deformity generally is the result of bursitis caused by pressure against the shoe, and can be aggravated by the height or stitching of a heel counter of a particular shoe. Pain at the back of the heel is associated with inflammation of the Achilles tendon as it runs behind the ankle and inserts on the back surface of the heel bone. The inflammation is called Achilles tendinitis. It is common among people who run and walk a lot and have tight tendons. The condition occurs when the tendon is strained over time, causing the fibbers to tear or stretch along its length, or at its insertion on to the heel bone. This leads to inflammation, pain, and the possible growth of a bone spur on the back of the heel bone. The inflammation is aggravated by the chronic irritation that sometimes accompanies an active lifestyle and certain activities that strain an already tight tendon. Bone bruises (Periostitis), are also common heel injuries. A bone bruise or contusion is an inflammation of the tissues that cover the heel bone. A bone bruise is a sharply painful injury caused by the direct impact of a hard object or surface on the foot. Stress fractures of the heel bone also can occur, but these are less frequent. On very rare occasions, there can be problems within the bone structure itself that cause heel pain. Paget's disease, cysts, bone tumours, and other conditions can occur in the heel causing pain, so it is important to be examined thoroughly.
Symptoms
Usually when a patient comes in they?ll explain that they have severe pain in the heel. It?s usually worse during the first step in the morning when they get out of bed. Many people say if they walk for a period of time, it gets a little bit better. But if they sit down and get back up, the pain will come back and it?s one of those intermittent come and go types of pain. Heel pain patients will say it feels like a toothache in the heel area or even into the arch area. A lot of times it will get better with rest and then it will just come right back. So it?s one of those nuisance type things that just never goes away. The following are common signs of heel pain and plantar fasciitis. Pain that is worse first thing in the morning. Pain that develops after heavy activity or exercise. Pain that occurs when standing up after sitting for a long period of time. Severe, toothache type of pain in the bottom of the heel.
Diagnosis
Your doctor will listen to your complaints about your heel and examine you to see what is causing the pain, and whether anything else has started it off. If the cause of your pain seems obvious, your doctor may be happy to start treatment straight away. However, some tests may be helpful in ruling out other problems. Blood tests may be done for arthritis. An Xray will show any arthritis in the ankle or subtalar joint, as well as any fracture or cyst in the calcaneum. (It will also show a spur if you have one, but as we know this is not the cause of the pain.) Occasionally a scan may be used to help spot arthritis or a stress fracture.
Non Surgical Treatment
There are many treatments for fasciitis. The most common initial treatment provided by the family doctor are anti-inflammatory medications. They may take the edge off the pain, but they don't often resolve the condition fully. Steroid injections, which deliver the medication directly to the most painful area, are usually more effective. Rest, ice, weight loss, taping, strapping, immobilization, physiotherapy, massage, stretching, heel cushions, acupuncture, night splints and extra-corporeal shock wave therapy all help some patients. Many patients, however, have a biomechanical cause such as excessively pronated feet to their complaint, and this may mean many of the treatments listed above will only provide temporary relief of fasciitis symptoms. When you stop the treatment, the pain often returns. This is why many cases of fasciitis respond well to orthoses, custom-made inserts that control the mechanical cause of the complaint. If you're considering orthoses, it's very important to have a podiatrist specializing in the field to examine you. There are many biomechanical factors to consider when assessing the need for literally dozens of types of devices available, so you need to have an expert to properly assess you. (Unfortunately, as is the case in many jurisdictions, there is no minimum standard of training required in British Columbia to make orthoses, and there are many fly-by-night operations around that employ salesmen with little, if any, training in understanding anatomy or foot function. The emphasis with these groups is on selling you some sort of device, rather than providing proper assessment, treatment and follow-up.
Surgical Treatment
Although most patients with plantar fasciitis respond to non-surgical treatment, a small percentage of patients may require surgery. If, after several months of non-surgical treatment, you continue to have heel pain, surgery will be considered. Your foot and ankle surgeon will discuss the surgical options with you and determine which approach would be most beneficial for you. No matter what kind of treatment you undergo for plantar fasciitis, the underlying causes that led to this condition may remain. Therefore, you will need to continue with preventive measures. Wearing supportive shoes, stretching, and using custom orthotic devices are the mainstay of long-term treatment for plantar fasciitis.
heel cups for achilles tendonitis
Prevention

Preventing heel pain is crucial to avoid pain that can easily interrupt a busy or active lifestyle. Athletes can prevent damage by stretching the foot and calf both before and after an exercise routine. The plantar fascia ligament can be stretched by using a tennis ball or water bottle and rolling it across the bottom of the foot. With regular stretching, the stretching and flexibility of tissue through the foot can be significantly improved, helping to prevent damage and injury. Athletes should also ease into new or more difficult routines, allowing the plantar fascia and other tissue to become accustomed to the added stress and difficulty. Running up hills is also common among athletes in their routines. However, this activity should be reduced since it places an increased amount of stress on the plantar fascia and increases the risk of plantar fasciitis. Maintaining a healthy weight is also an essential heel pain prevention technique. Obesity brings additional weight and stress on the heel of the foot, causing damage and pain in the heel as well as in other areas of the foot.

When walking, your heels repeatedly hit the ground with considerable force. They have to be able to absorb the impact and provide a firm support for the weight of the body. When pain develops in the heel, it can be very disabling, making every step a problem, affecting your posture. There are various types of heel pain. Some of the most common are: heel spurs (plantar fasciitis); heel bursitis and heel bumps.
Causes
Rheumatoid arthritis and other forms of arthritis, including gout, which usually manifests itself in the big toe joint, can cause heel discomfort in some cases. Heel pain may also be the result of an inflamed bursa (bursitis), a small, irritated sack of fluid behind the heel. A neuroma (a nerve growth) involving the so-called Baxter's Nerve, (a nerve that courses under the heel bone), may also cause heel pain that mimics the pain of a heel spur. Tarsal Tunnel Syndrome, a pinched nerve beneath the inside ankle bone, too, can cause pain in the heel. Haglund's deformity ("pump bump") is a bone enlargement at the back of the heel bone, in the area where the Achilles tendon attaches to the bone. This sometimes painful deformity generally is the result of bursitis caused by pressure against the shoe, and can be aggravated by the height or stitching of a heel counter of a particular shoe. Pain at the back of the heel is associated with inflammation of the Achilles tendon as it runs behind the ankle and inserts on the back surface of the heel bone. The inflammation is called Achilles tendinitis. It is common among people who run and walk a lot and have tight tendons. The condition occurs when the tendon is strained over time, causing the fibbers to tear or stretch along its length, or at its insertion on to the heel bone. This leads to inflammation, pain, and the possible growth of a bone spur on the back of the heel bone. The inflammation is aggravated by the chronic irritation that sometimes accompanies an active lifestyle and certain activities that strain an already tight tendon. Bone bruises (Periostitis), are also common heel injuries. A bone bruise or contusion is an inflammation of the tissues that cover the heel bone. A bone bruise is a sharply painful injury caused by the direct impact of a hard object or surface on the foot. Stress fractures of the heel bone also can occur, but these are less frequent. On very rare occasions, there can be problems within the bone structure itself that cause heel pain. Paget's disease, cysts, bone tumours, and other conditions can occur in the heel causing pain, so it is important to be examined thoroughly.
Symptoms
Usually when a patient comes in they?ll explain that they have severe pain in the heel. It?s usually worse during the first step in the morning when they get out of bed. Many people say if they walk for a period of time, it gets a little bit better. But if they sit down and get back up, the pain will come back and it?s one of those intermittent come and go types of pain. Heel pain patients will say it feels like a toothache in the heel area or even into the arch area. A lot of times it will get better with rest and then it will just come right back. So it?s one of those nuisance type things that just never goes away. The following are common signs of heel pain and plantar fasciitis. Pain that is worse first thing in the morning. Pain that develops after heavy activity or exercise. Pain that occurs when standing up after sitting for a long period of time. Severe, toothache type of pain in the bottom of the heel.
Diagnosis
Your doctor will listen to your complaints about your heel and examine you to see what is causing the pain, and whether anything else has started it off. If the cause of your pain seems obvious, your doctor may be happy to start treatment straight away. However, some tests may be helpful in ruling out other problems. Blood tests may be done for arthritis. An Xray will show any arthritis in the ankle or subtalar joint, as well as any fracture or cyst in the calcaneum. (It will also show a spur if you have one, but as we know this is not the cause of the pain.) Occasionally a scan may be used to help spot arthritis or a stress fracture.
Non Surgical Treatment
There are many treatments for fasciitis. The most common initial treatment provided by the family doctor are anti-inflammatory medications. They may take the edge off the pain, but they don't often resolve the condition fully. Steroid injections, which deliver the medication directly to the most painful area, are usually more effective. Rest, ice, weight loss, taping, strapping, immobilization, physiotherapy, massage, stretching, heel cushions, acupuncture, night splints and extra-corporeal shock wave therapy all help some patients. Many patients, however, have a biomechanical cause such as excessively pronated feet to their complaint, and this may mean many of the treatments listed above will only provide temporary relief of fasciitis symptoms. When you stop the treatment, the pain often returns. This is why many cases of fasciitis respond well to orthoses, custom-made inserts that control the mechanical cause of the complaint. If you're considering orthoses, it's very important to have a podiatrist specializing in the field to examine you. There are many biomechanical factors to consider when assessing the need for literally dozens of types of devices available, so you need to have an expert to properly assess you. (Unfortunately, as is the case in many jurisdictions, there is no minimum standard of training required in British Columbia to make orthoses, and there are many fly-by-night operations around that employ salesmen with little, if any, training in understanding anatomy or foot function. The emphasis with these groups is on selling you some sort of device, rather than providing proper assessment, treatment and follow-up.
Surgical Treatment
Although most patients with plantar fasciitis respond to non-surgical treatment, a small percentage of patients may require surgery. If, after several months of non-surgical treatment, you continue to have heel pain, surgery will be considered. Your foot and ankle surgeon will discuss the surgical options with you and determine which approach would be most beneficial for you. No matter what kind of treatment you undergo for plantar fasciitis, the underlying causes that led to this condition may remain. Therefore, you will need to continue with preventive measures. Wearing supportive shoes, stretching, and using custom orthotic devices are the mainstay of long-term treatment for plantar fasciitis.
heel cups for achilles tendonitis
Prevention

Preventing heel pain is crucial to avoid pain that can easily interrupt a busy or active lifestyle. Athletes can prevent damage by stretching the foot and calf both before and after an exercise routine. The plantar fascia ligament can be stretched by using a tennis ball or water bottle and rolling it across the bottom of the foot. With regular stretching, the stretching and flexibility of tissue through the foot can be significantly improved, helping to prevent damage and injury. Athletes should also ease into new or more difficult routines, allowing the plantar fascia and other tissue to become accustomed to the added stress and difficulty. Running up hills is also common among athletes in their routines. However, this activity should be reduced since it places an increased amount of stress on the plantar fascia and increases the risk of plantar fasciitis. Maintaining a healthy weight is also an essential heel pain prevention technique. Obesity brings additional weight and stress on the heel of the foot, causing damage and pain in the heel as well as in other areas of the foot.
Structural Leg Length Discrepancy Test
Overview
While many people have slight differences in the length of one leg compared to the other, a significant difference between the two legs can cause problems. Leg length discrepancies can disturb the way a person walks, how his or her spine lines up and strain hip joints.
Causes
An anatomical short leg is due to several orthopedic or medical condition mechanisms. Often, one leg simply stops growing before the other one does and is called ?congenital?. We often see mother-daughters or father-sons who exhibit virtually the same degree of shortness on the same side. Often it is not known why this occurs, but it seems to account for approximately 25% of the population demonstrating a true LLD. Other causes of a true LLD include trauma or broken bones, surgical repair, joint replacement, radiation exposure, tumors or Legg-Calves-Perthes disease.
Symptoms
LLD do not have any pain or discomfort directly associated with the difference of one leg over the other leg. However, LLD will place stress on joints throughout the skeletal structure of the body and create discomfort as a byproduct of the LLD. Just as it is normal for your feet to vary slightly in size, a mild difference in leg length is normal, too. A more pronounced LLD, however, can create abnormalities when walking or running and adversely affect healthy balance and posture. Symptoms include a slight limp. Walking can even become stressful, requiring more effort and energy. Sometimes knee pain, hip pain and lower back pain develop. Foot mechanics are also affected causing a variety of complications in the foot, not the least, over pronating, metatarsalgia, bunions, hammer toes, instep pain, posterior tibial tendonitis, and many more.
Diagnosis
A doctor will generally take a detailed medical history of both the patient and family, including asking about recent injuries or illnesses. He or she will carefully examine the patient, observing how he or she moves and stands. If necessary, an orthopedic surgeon will order X-ray, bone age determinations and computed tomography (CT) scans or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI).
Non Surgical Treatment
Treatment depends on what limb has the deformity and the amount of deformity present. For example, there may be loss of function of the leg or arm. Cosmetic issues may also be a concern for the patient and their family. If there are problems with the arms, the goal is to improve the appearance and function of the arm. Treatment of leg problems try to correct the deformity that may cause arthritis as the child gets older. If the problem is leg length, where the legs are not "equal," the goal is equalization (making the legs the same length). Treatment may include the use of adaptive devices, prosthesis, orthotics or shoe lifts. If the problem is more severe and not treatable with these methods, then surgery may be necessary.

what happens if one leg is shorter than the other?
Surgical Treatment
In growing children, legs can be made equal or nearly equal in length with a relatively simple surgical procedure. This procedure slows down the growth of the longer leg at one or two growth sites. Your physician can tell you how much equalization can be gained by this procedure. The procedure is performed under X-ray control through very small incisions in the knee area. This procedure will not cause an immediate correction in length. Instead, the limb length discrepancy will gradually decrease as the opposite extremity continues to grow and "catch up." Timing of the procedure is critical. The goal is to reach equal leg length by the time growth normally ends. This is usually in the mid-to-late teenage years. Disadvantages of this option include the possibility of slight over-correction or under-correction of the limb length discrepancy. In addition, the patient's adult height will be less than if the shorter leg had been lengthened. Correction of significant limb length discrepancy by this method may make a patient's body look slightly disproportionate because of the shorter leg. In some cases the longer leg can be shortened, but a major shortening may weaken the muscles of the leg. In the thighbone (femur), a maximum of 3 inches can be shortened. In the shinbone, a maximum of 2 inches can be shortened.
While many people have slight differences in the length of one leg compared to the other, a significant difference between the two legs can cause problems. Leg length discrepancies can disturb the way a person walks, how his or her spine lines up and strain hip joints.

Causes
An anatomical short leg is due to several orthopedic or medical condition mechanisms. Often, one leg simply stops growing before the other one does and is called ?congenital?. We often see mother-daughters or father-sons who exhibit virtually the same degree of shortness on the same side. Often it is not known why this occurs, but it seems to account for approximately 25% of the population demonstrating a true LLD. Other causes of a true LLD include trauma or broken bones, surgical repair, joint replacement, radiation exposure, tumors or Legg-Calves-Perthes disease.
Symptoms
LLD do not have any pain or discomfort directly associated with the difference of one leg over the other leg. However, LLD will place stress on joints throughout the skeletal structure of the body and create discomfort as a byproduct of the LLD. Just as it is normal for your feet to vary slightly in size, a mild difference in leg length is normal, too. A more pronounced LLD, however, can create abnormalities when walking or running and adversely affect healthy balance and posture. Symptoms include a slight limp. Walking can even become stressful, requiring more effort and energy. Sometimes knee pain, hip pain and lower back pain develop. Foot mechanics are also affected causing a variety of complications in the foot, not the least, over pronating, metatarsalgia, bunions, hammer toes, instep pain, posterior tibial tendonitis, and many more.
Diagnosis
A doctor will generally take a detailed medical history of both the patient and family, including asking about recent injuries or illnesses. He or she will carefully examine the patient, observing how he or she moves and stands. If necessary, an orthopedic surgeon will order X-ray, bone age determinations and computed tomography (CT) scans or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI).
Non Surgical Treatment
Treatment depends on what limb has the deformity and the amount of deformity present. For example, there may be loss of function of the leg or arm. Cosmetic issues may also be a concern for the patient and their family. If there are problems with the arms, the goal is to improve the appearance and function of the arm. Treatment of leg problems try to correct the deformity that may cause arthritis as the child gets older. If the problem is leg length, where the legs are not "equal," the goal is equalization (making the legs the same length). Treatment may include the use of adaptive devices, prosthesis, orthotics or shoe lifts. If the problem is more severe and not treatable with these methods, then surgery may be necessary.

what happens if one leg is shorter than the other?
Surgical Treatment
In growing children, legs can be made equal or nearly equal in length with a relatively simple surgical procedure. This procedure slows down the growth of the longer leg at one or two growth sites. Your physician can tell you how much equalization can be gained by this procedure. The procedure is performed under X-ray control through very small incisions in the knee area. This procedure will not cause an immediate correction in length. Instead, the limb length discrepancy will gradually decrease as the opposite extremity continues to grow and "catch up." Timing of the procedure is critical. The goal is to reach equal leg length by the time growth normally ends. This is usually in the mid-to-late teenage years. Disadvantages of this option include the possibility of slight over-correction or under-correction of the limb length discrepancy. In addition, the patient's adult height will be less than if the shorter leg had been lengthened. Correction of significant limb length discrepancy by this method may make a patient's body look slightly disproportionate because of the shorter leg. In some cases the longer leg can be shortened, but a major shortening may weaken the muscles of the leg. In the thighbone (femur), a maximum of 3 inches can be shortened. In the shinbone, a maximum of 2 inches can be shortened.
Mortons Neuroma Causes
Overview
 A neuroma develops when a nerve is compressed, injured or pinched, causing swelling and pain. A neuroma in the area between the third and fourth toes, or between the second and third toes, is known as a Morton?s neuroma. Morton?s neuroma causes sharp, burning pain and numbness in the toes and foot. You may feel like you?ve stepped on a tiny hot coal and can?t get rid of it. At the same time, you?ll have the disconcerting experience of not being able to feel your toes. Sometimes the nerve tissue becomes so thickened you can feel or see a lump.
A neuroma develops when a nerve is compressed, injured or pinched, causing swelling and pain. A neuroma in the area between the third and fourth toes, or between the second and third toes, is known as a Morton?s neuroma. Morton?s neuroma causes sharp, burning pain and numbness in the toes and foot. You may feel like you?ve stepped on a tiny hot coal and can?t get rid of it. At the same time, you?ll have the disconcerting experience of not being able to feel your toes. Sometimes the nerve tissue becomes so thickened you can feel or see a lump.
Causes
Experts are not sure what exactly causes Morton's neuroma. It seems to develop as a result of irritation, pressure or injury to one of the digital nerves that lead to the toes, which triggers a body response, resulting in thickened nerve tissue (neuroma). Feet conditions/situations that can cause the bones to rub against a nerve include high-heeled shoes, especially those over 2 inches (5cm), or a pointed or tight toe box which squash the toes together. This is probably why the condition is much more common in females than in males. High-arched foot, people whose feet have high arches are much more likely to suffer from Morton's neuroma than others. Flat feet, the arch of the foot collapses. The entire sole of the foot comes into complete or near-complete contact with the ground. A bunion, a localized painful swelling at the base of the big toe, which enlarges the joint. Hammer toe, a deformity of the proximal interphalangeal joint of the second, third, or fourth toe causing it to be permanently bent. Some high-impact sporting activities including running, karate, and court sports. Any sport that places undue pressure on the feet. Injuries, an injury or other type of trauma to the foot may lead to a neuroma.
Symptoms
If you have a Morton?s neuroma, you may have one or more of these symptoms where the nerve damage is occurring, Tingling, burning, or numbness, pain, a feeling that something is inside the ball of the foot or a feeling that there?s something in the shoe or a sock is bunched up. The progression of a Morton?s neuroma often follows the following pattern. The symptoms begin gradually. At first they occur only occasionally, when wearing narrow-toed shoes or performing certain aggravating activities. The symptoms may go away temporarily by removing the shoe, massaging the foot, or by avoiding aggravating shoes or activities. Over time the symptoms progressively worsen and may persist for several days or weeks. The symptoms become more intense as the neuroma enlarges and the temporary changes in the nerve become permanent.
Diagnosis
In some cases your doctor will be able to feel the Morton's as a swelling in the middle of your foot. However they may also suggest an X-ray or a blood test - this is normally to rule our other causes of the pain such as arthritis. The most accurate way to diagnose Morton?s itself is with magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) or ultrasound.
Non Surgical Treatment
Sclerosing alcohol injections are an increasingly available treatment alternative if the above management approaches fail. Dilute alcohol (4%) is injected directly into the area of the neuroma, causing toxicity to the fibrous nerve tissue. Frequently, treatment must be performed 2-4 times, with 1-3 weeks between interventions. An 60-80% success rate has been achieved in clinical studies, equal to or exceeding the success rate for surgical neurectomy with fewer risks and less significant recovery. If done with more concentrated alcohol under ultrasound guidance, the success rate is considerably higher and fewer repeat procedures are needed. Radio Frequency Ablation is also used in the treatment of Morton's Neuroma The outcomes appear to be equally or more reliable than alcohol injections especially if the procedure is done under ultrasound guidance.
Surgical Treatment
Surgery is occasionally required when the conservative treatment is not able to relieve your symptoms, particularly if you have had pain for more than 6 months. 80% of patients who require surgery report good results, with 71% of people becoming pain-free.
 A neuroma develops when a nerve is compressed, injured or pinched, causing swelling and pain. A neuroma in the area between the third and fourth toes, or between the second and third toes, is known as a Morton?s neuroma. Morton?s neuroma causes sharp, burning pain and numbness in the toes and foot. You may feel like you?ve stepped on a tiny hot coal and can?t get rid of it. At the same time, you?ll have the disconcerting experience of not being able to feel your toes. Sometimes the nerve tissue becomes so thickened you can feel or see a lump.
A neuroma develops when a nerve is compressed, injured or pinched, causing swelling and pain. A neuroma in the area between the third and fourth toes, or between the second and third toes, is known as a Morton?s neuroma. Morton?s neuroma causes sharp, burning pain and numbness in the toes and foot. You may feel like you?ve stepped on a tiny hot coal and can?t get rid of it. At the same time, you?ll have the disconcerting experience of not being able to feel your toes. Sometimes the nerve tissue becomes so thickened you can feel or see a lump.Causes
Experts are not sure what exactly causes Morton's neuroma. It seems to develop as a result of irritation, pressure or injury to one of the digital nerves that lead to the toes, which triggers a body response, resulting in thickened nerve tissue (neuroma). Feet conditions/situations that can cause the bones to rub against a nerve include high-heeled shoes, especially those over 2 inches (5cm), or a pointed or tight toe box which squash the toes together. This is probably why the condition is much more common in females than in males. High-arched foot, people whose feet have high arches are much more likely to suffer from Morton's neuroma than others. Flat feet, the arch of the foot collapses. The entire sole of the foot comes into complete or near-complete contact with the ground. A bunion, a localized painful swelling at the base of the big toe, which enlarges the joint. Hammer toe, a deformity of the proximal interphalangeal joint of the second, third, or fourth toe causing it to be permanently bent. Some high-impact sporting activities including running, karate, and court sports. Any sport that places undue pressure on the feet. Injuries, an injury or other type of trauma to the foot may lead to a neuroma.
Symptoms
If you have a Morton?s neuroma, you may have one or more of these symptoms where the nerve damage is occurring, Tingling, burning, or numbness, pain, a feeling that something is inside the ball of the foot or a feeling that there?s something in the shoe or a sock is bunched up. The progression of a Morton?s neuroma often follows the following pattern. The symptoms begin gradually. At first they occur only occasionally, when wearing narrow-toed shoes or performing certain aggravating activities. The symptoms may go away temporarily by removing the shoe, massaging the foot, or by avoiding aggravating shoes or activities. Over time the symptoms progressively worsen and may persist for several days or weeks. The symptoms become more intense as the neuroma enlarges and the temporary changes in the nerve become permanent.
Diagnosis
In some cases your doctor will be able to feel the Morton's as a swelling in the middle of your foot. However they may also suggest an X-ray or a blood test - this is normally to rule our other causes of the pain such as arthritis. The most accurate way to diagnose Morton?s itself is with magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) or ultrasound.
Non Surgical Treatment
Sclerosing alcohol injections are an increasingly available treatment alternative if the above management approaches fail. Dilute alcohol (4%) is injected directly into the area of the neuroma, causing toxicity to the fibrous nerve tissue. Frequently, treatment must be performed 2-4 times, with 1-3 weeks between interventions. An 60-80% success rate has been achieved in clinical studies, equal to or exceeding the success rate for surgical neurectomy with fewer risks and less significant recovery. If done with more concentrated alcohol under ultrasound guidance, the success rate is considerably higher and fewer repeat procedures are needed. Radio Frequency Ablation is also used in the treatment of Morton's Neuroma The outcomes appear to be equally or more reliable than alcohol injections especially if the procedure is done under ultrasound guidance.

Surgical Treatment
Surgery is occasionally required when the conservative treatment is not able to relieve your symptoms, particularly if you have had pain for more than 6 months. 80% of patients who require surgery report good results, with 71% of people becoming pain-free.
Leg Length Discrepancy And Shoe Lifts
There are actually not one but two different types of leg length discrepancies, congenital and acquired. Congenital implies that you are born with it. One leg is structurally shorter compared to the other. As a result of developmental phases of aging, the human brain picks up on the stride pattern and identifies some difference. Your body typically adapts by tilting one shoulder over to the "short" side. A difference of less than a quarter inch isn't very uncommon, does not need Shoe Lifts to compensate and typically won't have a profound effect over a lifetime.

Leg length inequality goes typically undiagnosed on a daily basis, however this problem is simply remedied, and can eliminate a number of instances of lower back pain.
Treatment for leg length inequality commonly involves Shoe Lifts. They are affordable, in most cases costing less than twenty dollars, in comparison to a custom orthotic of $200 or maybe more. When the amount of leg length inequality begins to exceed half an inch, a whole sole lift is generally the better choice than a heel lift. This prevents the foot from being unnecessarily stressed in an abnormal position.
Low back pain is easily the most widespread ailment afflicting people today. Over 80 million men and women experience back pain at some stage in their life. It is a problem which costs businesses millions of dollars annually as a result of lost time and production. New and improved treatment methods are always sought after in the hope of minimizing the economical influence this condition causes.

Men and women from all corners of the world suffer from foot ache as a result of leg length discrepancy. In a lot of these cases Shoe Lifts might be of very useful. The lifts are capable of alleviating any pain and discomfort in the feet. Shoe Lifts are recommended by countless specialist orthopaedic practitioners".
So as to support the human body in a nicely balanced manner, the feet have got a vital function to play. Despite that, it can be the most neglected zone of the human body. Some people have flat-feet which means there is unequal force exerted on the feet. This will cause other parts of the body including knees, ankles and backs to be impacted too. Shoe Lifts make sure that appropriate posture and balance are restored.

Leg length inequality goes typically undiagnosed on a daily basis, however this problem is simply remedied, and can eliminate a number of instances of lower back pain.
Treatment for leg length inequality commonly involves Shoe Lifts. They are affordable, in most cases costing less than twenty dollars, in comparison to a custom orthotic of $200 or maybe more. When the amount of leg length inequality begins to exceed half an inch, a whole sole lift is generally the better choice than a heel lift. This prevents the foot from being unnecessarily stressed in an abnormal position.
Low back pain is easily the most widespread ailment afflicting people today. Over 80 million men and women experience back pain at some stage in their life. It is a problem which costs businesses millions of dollars annually as a result of lost time and production. New and improved treatment methods are always sought after in the hope of minimizing the economical influence this condition causes.

Men and women from all corners of the world suffer from foot ache as a result of leg length discrepancy. In a lot of these cases Shoe Lifts might be of very useful. The lifts are capable of alleviating any pain and discomfort in the feet. Shoe Lifts are recommended by countless specialist orthopaedic practitioners".
So as to support the human body in a nicely balanced manner, the feet have got a vital function to play. Despite that, it can be the most neglected zone of the human body. Some people have flat-feet which means there is unequal force exerted on the feet. This will cause other parts of the body including knees, ankles and backs to be impacted too. Shoe Lifts make sure that appropriate posture and balance are restored.
Shoe Lifts The Podiatrists Solution For Leg Length Imbalances
There are actually two different types of leg length discrepancies, congenital and acquired. Congenital indicates that you are born with it. One leg is anatomically shorter than the other. Through developmental phases of aging, the human brain picks up on the stride pattern and identifies some difference. The human body usually adapts by dipping one shoulder over to the "short" side. A difference of less than a quarter inch is not grossly irregular, require Shoe Lifts to compensate and mostly won't have a profound effect over a lifetime.

Leg length inequality goes largely undiscovered on a daily basis, yet this problem is simply fixed, and can eliminate many cases of back discomfort.
Treatment for leg length inequality commonly involves Shoe Lifts. These are cost-effective, generally costing below twenty dollars, in comparison to a custom orthotic of $200 plus. Differences over a quarter inch can take their toll on the spine and should probably be compensated for with a heel lift. In some cases, the shortage can be so extreme that it requires a full lift to both the heel and sole of the shoe.
Back ache is the most widespread condition affecting people today. Over 80 million men and women are afflicted by back pain at some point in their life. It is a problem which costs companies huge amounts of money every year on account of time lost and productivity. Innovative and better treatment methods are constantly sought after in the hope of reducing the economic impact this condition causes.

People from all corners of the earth experience foot ache due to leg length discrepancy. In these types of cases Shoe Lifts are usually of immense help. The lifts are capable of eliminating any discomfort in the feet. Shoe Lifts are recommended by countless qualified orthopaedic practitioners".
So that they can support the body in a healthy and balanced manner, your feet have got a crucial task to play. In spite of that, it is sometimes the most overlooked zone in the body. Many people have flat-feet which means there may be unequal force exerted on the feet. This will cause other parts of the body such as knees, ankles and backs to be impacted too. Shoe Lifts make sure that appropriate posture and balance are restored.

Leg length inequality goes largely undiscovered on a daily basis, yet this problem is simply fixed, and can eliminate many cases of back discomfort.
Treatment for leg length inequality commonly involves Shoe Lifts. These are cost-effective, generally costing below twenty dollars, in comparison to a custom orthotic of $200 plus. Differences over a quarter inch can take their toll on the spine and should probably be compensated for with a heel lift. In some cases, the shortage can be so extreme that it requires a full lift to both the heel and sole of the shoe.
Back ache is the most widespread condition affecting people today. Over 80 million men and women are afflicted by back pain at some point in their life. It is a problem which costs companies huge amounts of money every year on account of time lost and productivity. Innovative and better treatment methods are constantly sought after in the hope of reducing the economic impact this condition causes.

People from all corners of the earth experience foot ache due to leg length discrepancy. In these types of cases Shoe Lifts are usually of immense help. The lifts are capable of eliminating any discomfort in the feet. Shoe Lifts are recommended by countless qualified orthopaedic practitioners".
So that they can support the body in a healthy and balanced manner, your feet have got a crucial task to play. In spite of that, it is sometimes the most overlooked zone in the body. Many people have flat-feet which means there may be unequal force exerted on the feet. This will cause other parts of the body such as knees, ankles and backs to be impacted too. Shoe Lifts make sure that appropriate posture and balance are restored.
Contracted Toe Tendon Surgery Treatment
 Overview
Overview
A hammertoe occurs when the joint of the toes curl down. The reason they curl abnormally is due to a muscle imbalance which results in the tendons becoming unnaturally tight. They are due to Heredity, improper shoes, and Arthritis. There are two types of hammer toes, flexible or rigid. These classification are based on the mobility of the toe joints. A flexible hammer toe is one with a flexible toe joint that allows it to be straightend with your finger. In time a flexible joint may turn into a rigid hammer toe. Normally flexible hammer toes are much less painful than rigid hammer toes. A rigid hammer toe is one with a rigid toe joint, one that is not moveable with your finger. These rigid toe joints can be very painful and limit the ability to move.
Causes
Hammer toes are most frequently caused by a muscle - tendon imbalance in the foot, and are seen both in adults and children. Foot muscles work in pairs to straighten and bend the toes. If your foot has a biomechanical defect, the muscles tighten and the tendons shorten. Eventually, the toe muscles can?t straighten the toe, even when barefoot. Contributing factors are poor choices in footwear, arthritis, or trauma.
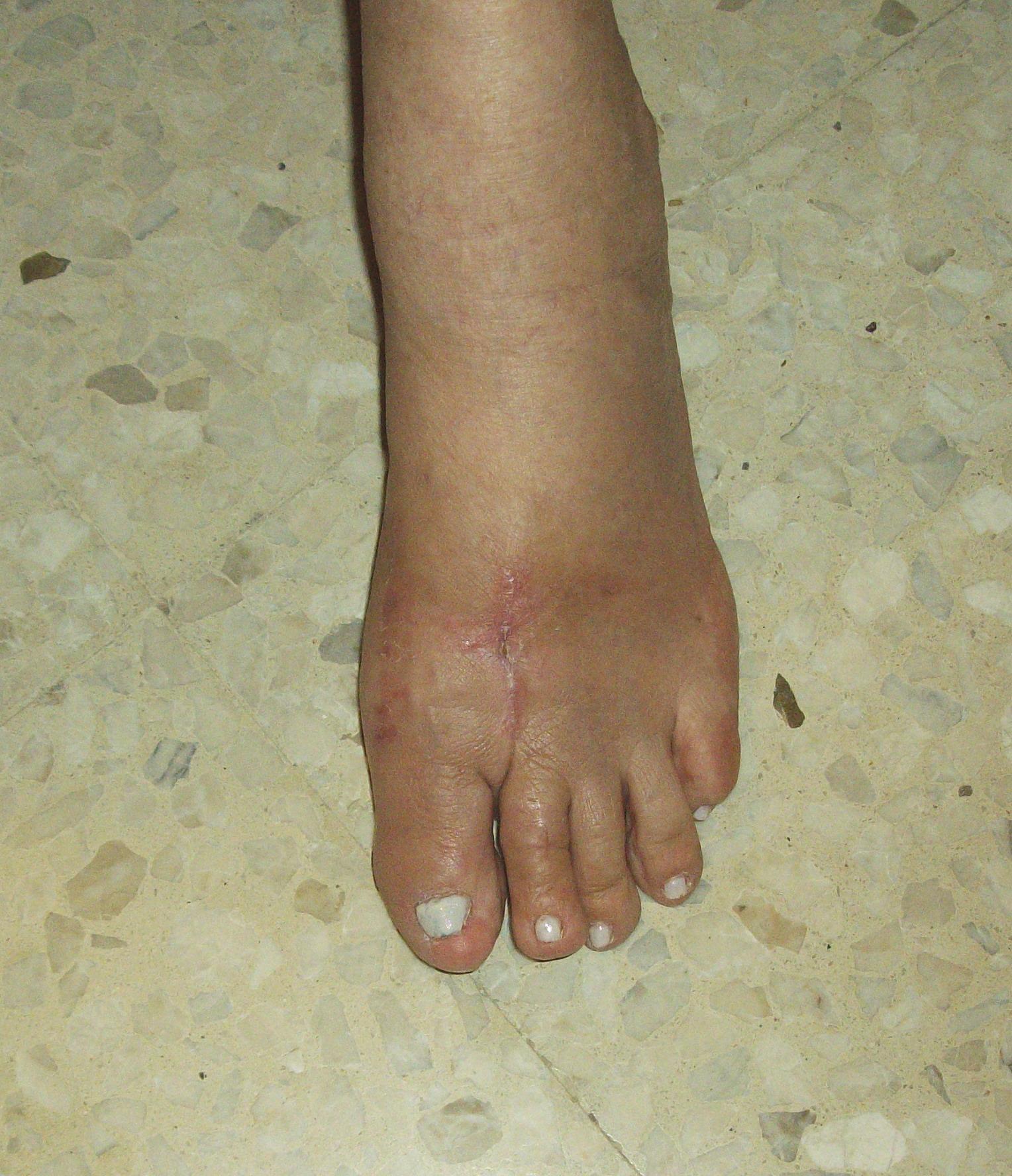
 Symptoms
Symptoms
A toe (usually the second digit, next to the big toe) bent at the middle joint and clenched into a painful, clawlike position. As the toe points downward, the middle joint may protrude upward. A toe with an end joint that curls under itself. Painful calluses or corns. Redness or a painful corn on top of the bent joint or at the tip of the affected toe, because of persistent rubbing against shoes Pain in the toes that interferes with walking, jogging, dancing, and other normal activities, possibly leading to gait changes.
Diagnosis
Most health care professionals can diagnose hammertoe simply by examining your toes and feet. X-rays of the feet are not needed to diagnose hammertoe, but they may be useful to look for signs of some types of arthritis (such as rheumatoid arthritis) or other disorders that can cause hammertoe.
Non Surgical Treatment
Conservative treatment starts with new shoes that have soft, roomy toe boxes. Shoes should be one-half inch longer than your longest toe. For many people, the second toe is longer than the big toe.) Avoid wearing tight, narrow, high-heeled shoes. You may also be able to find a shoe with a deep toe box that accommodates the hammer toe. Or, a shoe repair shop may be able to stretch the toe box so that it bulges out around the toe. Sandals may help, as long as they do not pinch or rub other areas of the foot.
Surgical Treatment
Ordinary hammertoe procedures often use exposed wires which extend outside the end of toes for 4-6 weeks. Common problems associated with wires include infection where the wires Hammer toes come out of the toe, breakage, pain from hitting the wire, and lack of rotational stability causing the toe to look crooked. In addition, wires require a second in-office procedure to remove them, which can cause a lot of anxiety for many patients. Once inserted, implants remain within the bone, correcting the pain and deformity of hammertoes while eliminating many of the complications specific traditional treatments.
 Prevention
Prevention
You can avoid many foot, heel and ankle problems with shoes that fit properly. See your doctor if you have foot pain that's persistent and that affects your ability to walk properly and carry out other motions with your foot. Also, see your doctor if one or more of your toes has developed a clenched or claw-like appearance.